Travellers can book online trains in Japan and receive the electronic tickets by email, ready for boarding.
We facilitate advance ticket booking for Shinkansen trains connecting Aomori, Sendai, Tokyo, Nagoya, Kyoto, Osaka, Kobe, Himeji, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi, Fukuoka, Kumamoto and Kagoshima, as well as Limited Express trains operated by JR Hokkaido, JR East and JR West connecting Sapporo, Hakodate, Hirosaki, Akita, Niigata, Nikko, Fuji, Matsumoto, Nagano and Kanazawa.
We also facilitate the purchase of different rail pass to travel on Shinkansen and Limited Express trains, as well as different tourist pass to travel on Express, Rapid or Local trains in Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku and Kyushu regions.
Contents
- Train companies in Japan
- Getting around Japan by train
- Destinations
- - Hokkaido island
- - Tohoku region
- - Train routes to Aomori
- - Train routes to Hirosaki
- - Train routes to Akita
- - Train routes to Sendai
- - Kanto region
- - Chubu region
- - Train routes to Fuji
- - Train routes to Shizuoka
- - Train routes to Nagoya
- - Train routes to Matsumoto
- - Train routes to Nagano
- - Train routes to Niigata
- - Train routes to Kanazawa
- - Kansai region
- - Train routes to Kyoto
- - Train routes to Osaka
- - Train routes to Nara
- - Train routes to Yoshino
- - Train routes to Kobe
- - Train routes to Himeji
- - Chugoku region
- - Kyushu island
- Getting around Tokyo by train and subway
- Getting around Osaka by train and subway
- How to book your train tickets in Japan?
Train companies in Japan
Rail services in Japan are operated by Japan Railways (JR) as well as private railway companies.
Japan Railways (JR) consists of several independent companies that carry on the operations of the former national railway operator JNR. In the present, JR Group is divided in six companies dedicated to provide passenger train services in different regions of Japan: JR Hokkaido, JR East, JR Central, JR West, JR Shikoku and JR Kyushu.
To achieve a complete coverage of the railway transportation across the nation, Japan Railways (JR) operates several types of intercity trains, including:
- - Shinkansen high-speed rail
- - Limited Express conventional rail
Shinkansen high-speed rail
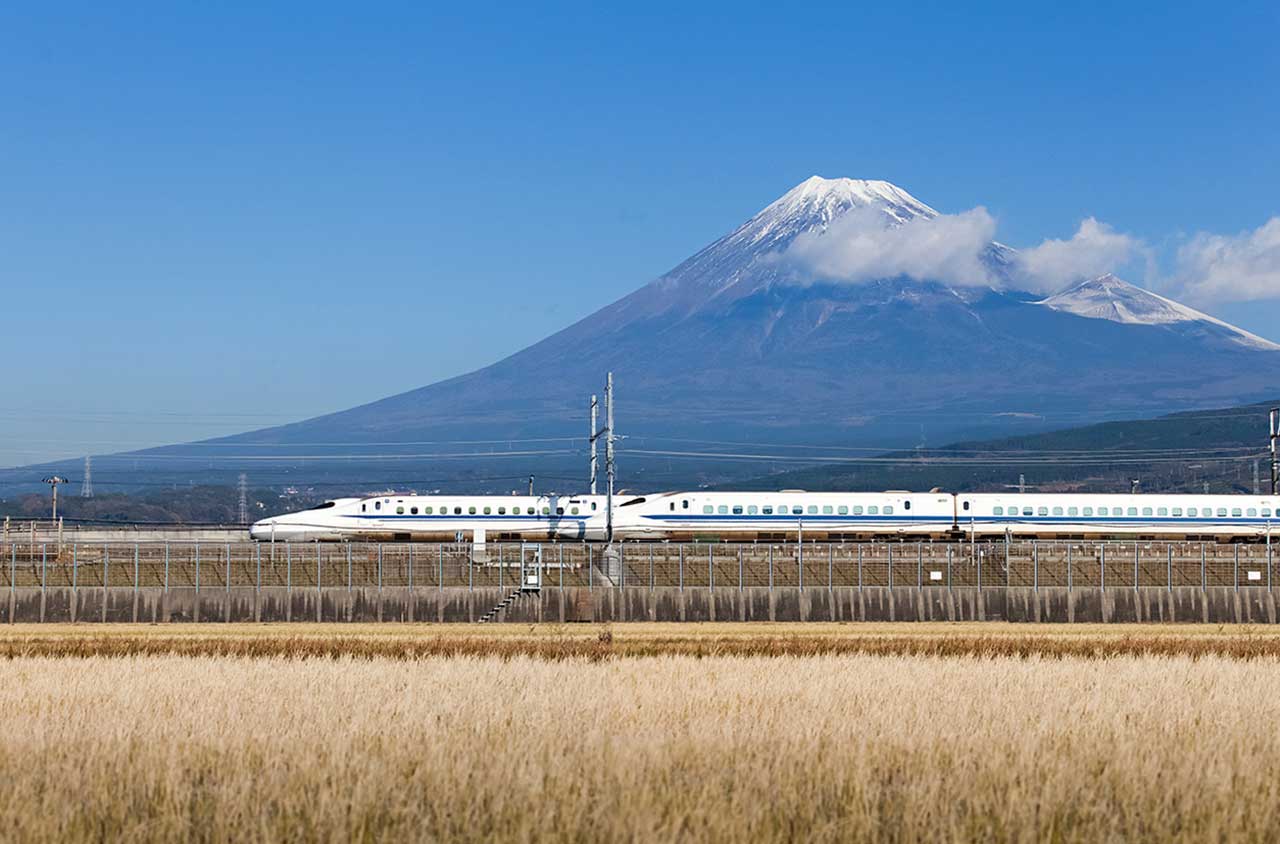
Shinkansen is the high-speed railway service operated by Japan Railways with trains running at a maximum speed of 240–320 km/h.
The Tokaido line was launched in 1964 connecting Tokyo, Nagoya and Osaka. Since then, the network has expanded to interconnect most of the major cities in the islands of Honshu, Hokkaido and Kyushu. The current Shinkansen network consists of 2,764 kilometers of dedicated high-speed tracks that use standard-gauge and are separated from the conventional lines that use different gauge.

The main Shinkansen lines are the following:
- - Tokaido Shinkansen between Tokyo and Osaka, operated by JR Central
- - Sanyo Shinkansen between Osaka and Fukuoka, operated by JR West
- - Kyushu Shinkansen between Fukuoka and Kagoshima, operated by JR Kyushu
- - Hokkaido Shinkansen between Aomori and Hokuto, operated by JR Hokkaido
- - Tohoku Shinkansen between Tokyo and Aomori, operated by JR East
- - Akita Shinkansen between Tokyo and Akita, operated by JR East
- - Yamagata Shinkansen between Tokyo and Shinjo, operated by JR East
- - Joetsu Shinkansen between Tokyo and Niigata, operated by JR East
- - Hokuriku Shinkansen between Tokyo and Tsuruga, jointly operated by JR East and JR West
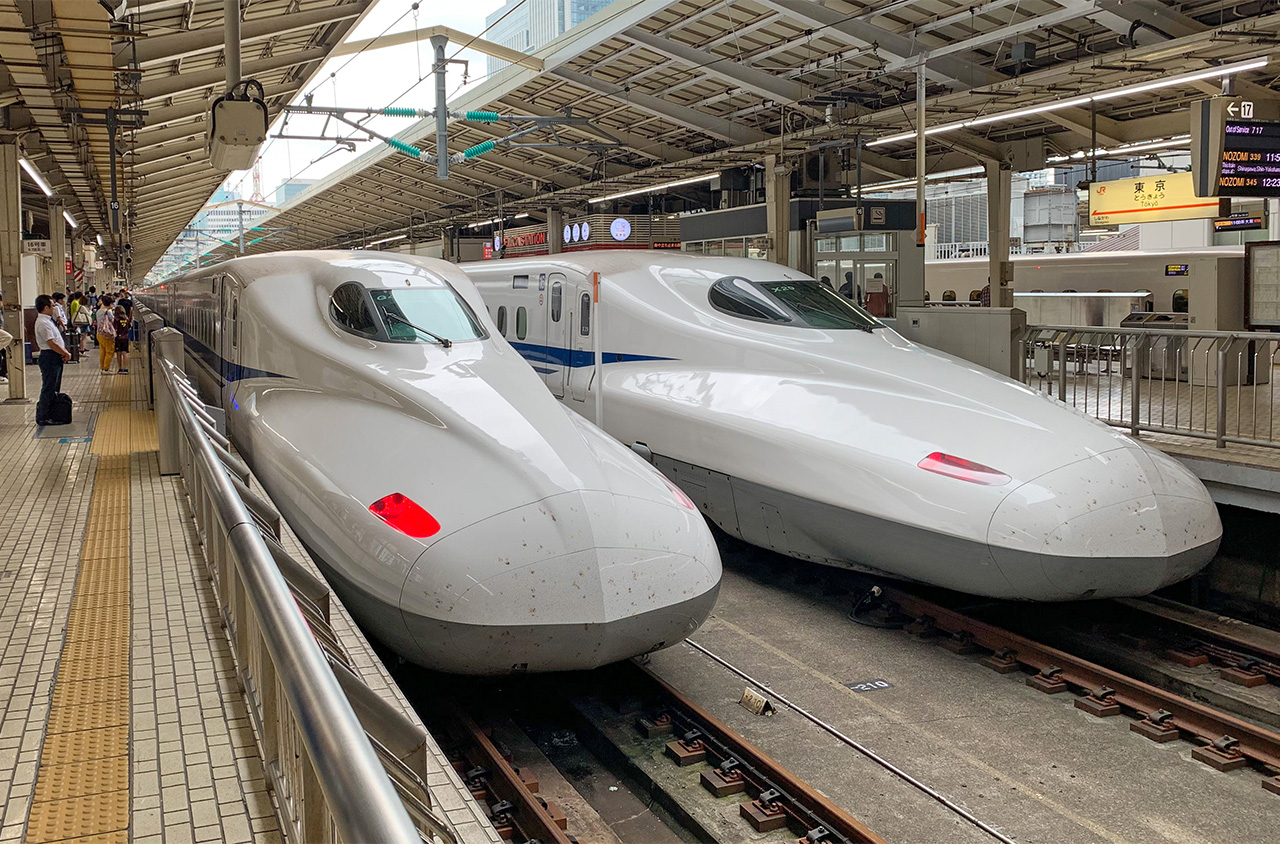
The Tokaido and Sanyo lines are interconnected forming a continuous corridor that links Tokyo, Osaka and Fukuoka, and is used by through services operated by JR Central and JR West. The Sanyo and Kyushu lines are interconnected forming a continuous corridor that links Osaka, Fukuoka and Kagoshima, and is used by through services operated by JR West and JR Kyushu.

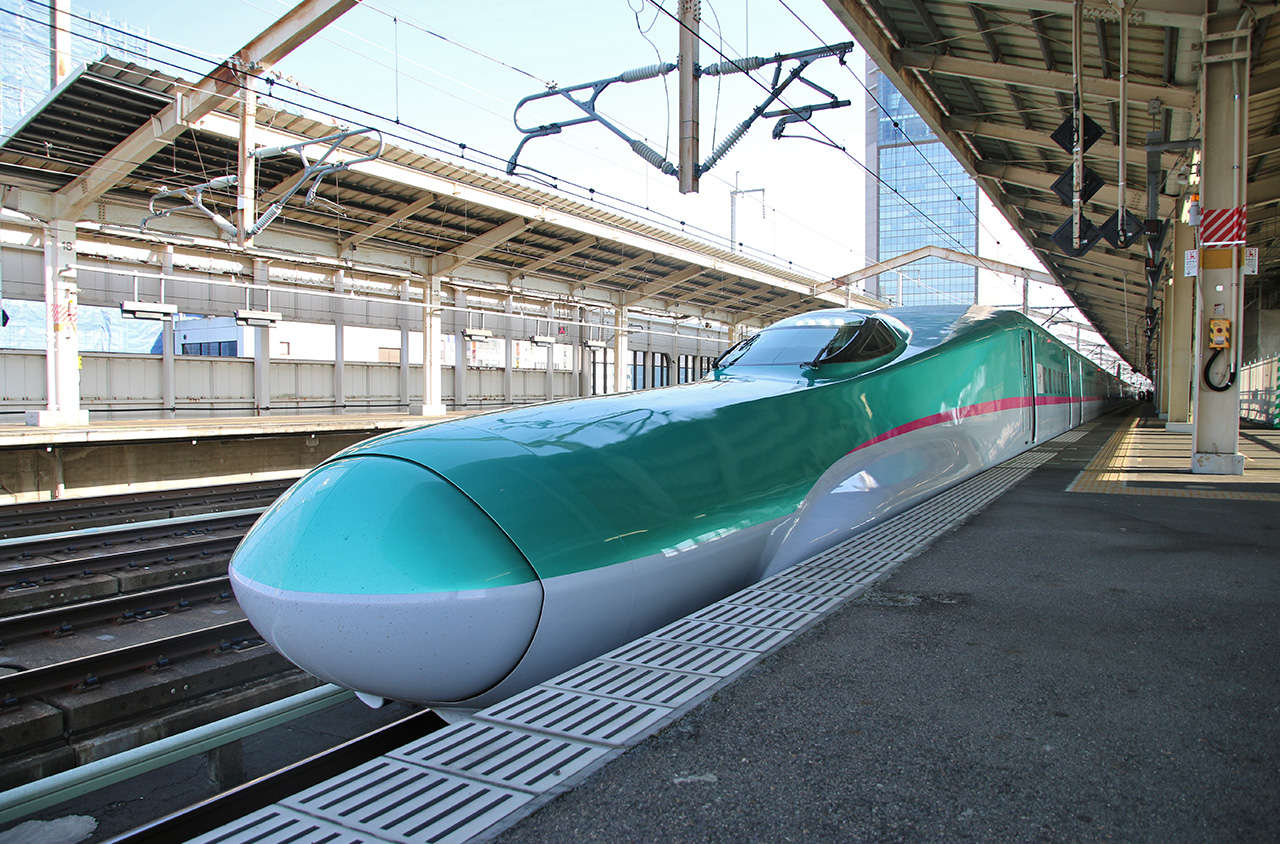
The Tohoku line and the Tokaido line meet in Tokyo but the tracks are not physically interconnected, hence there are no through services between the East and Central regions and passengers are required to interchange trains at Tokyo Station.

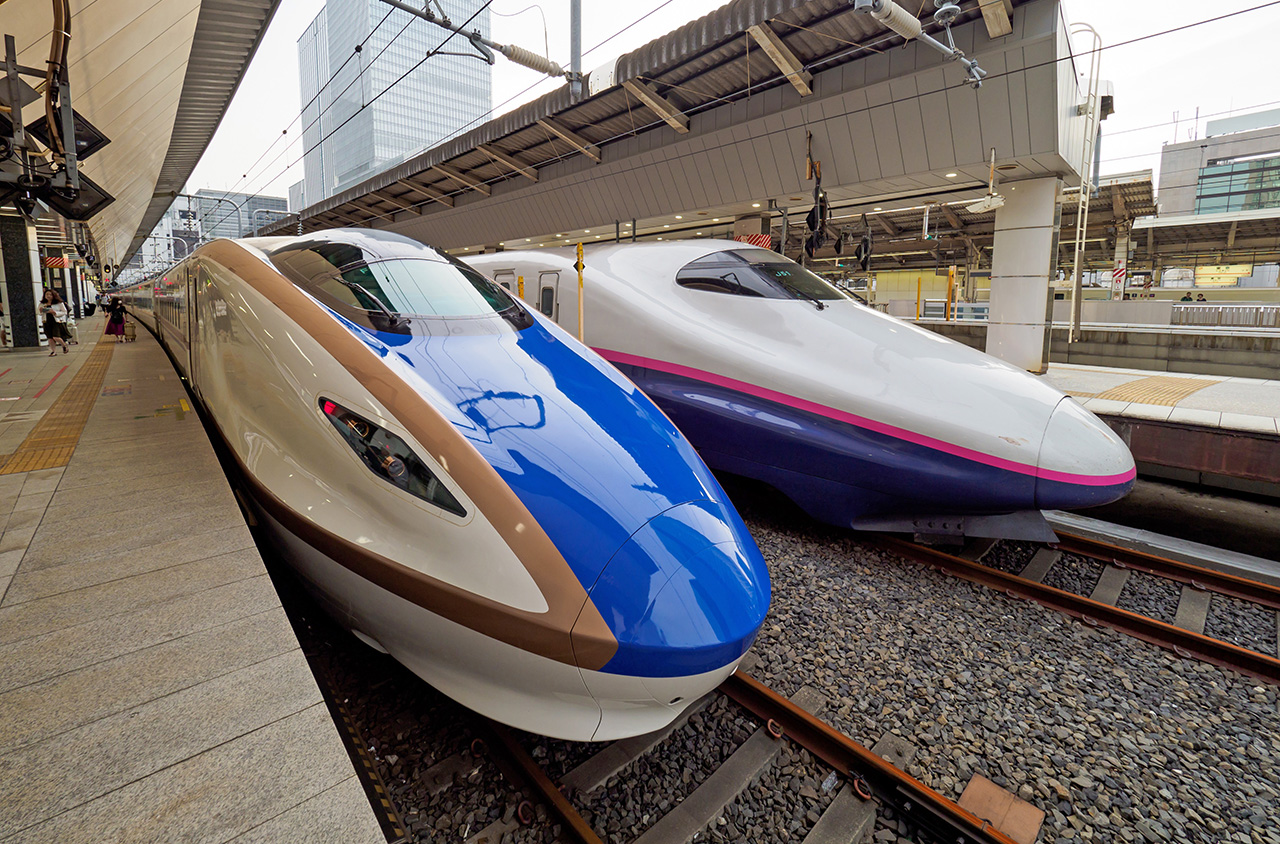
The Hokuriku line operates over the Joetsu and Tohoku lines tracks between Tokyo and Takasaki, then it separates and continues on its own dedicated tracks to Nagano and Kanazawa.

Shinkansen trains are designated by a code name that identifies the class of service followed by one to three numerals. The fast services stop only at key stations, the semi-fast services stop at the major stations, and the local services stop at all stations:
- - In the Tokaido and Sanyo lines, NOZOMI is the fast service, HIKARI is the semi-fast service and KODAMA is the local service.
- - In the Sanyo and Kyushu lines, MIZUHO is the fast service, SAKURA is the semi-fast service and TSUBAME is the local service.
- - In the Hokkaido line, HAYABUSA is the fast service and HAYATE is the semi-fast service.
- - In the Tohoku line, HAYABUSA is the fast service, YAMABIKO is the semi-fast service and NASUNO is the local service.
- - In the Akita line, KOMACHI is the fast service between Tokyo and Morioka, as well as the local service between Morioka and Akita.
- - In the Yamagata line, TSUBASA is the semi-fast service between Tokyo and Fukushima, as well as the local service between Fukushima and Shinjo.
- - In the Joetsu line, TOKI is the semi-fast service and TANIGAWA is the local service.
- - In the Hokuriku line, KAGAYAKI is the fast service, HAKUTAKA and ASAMA are the two semi-fast services, and TSURUGI is the local service.

Shinkansen trains are powered by electric multiple units and can carry up to 16 cars per train, arranged in Green Car with business class seats that require advanced reservation and Ordinary Car with standard class seats distributed in Reserved and Non-reserved.
In total, the Shinkansen trains offer three passengers classes: Green Car Seat, Reserved Seat and Non-reserved Seat.
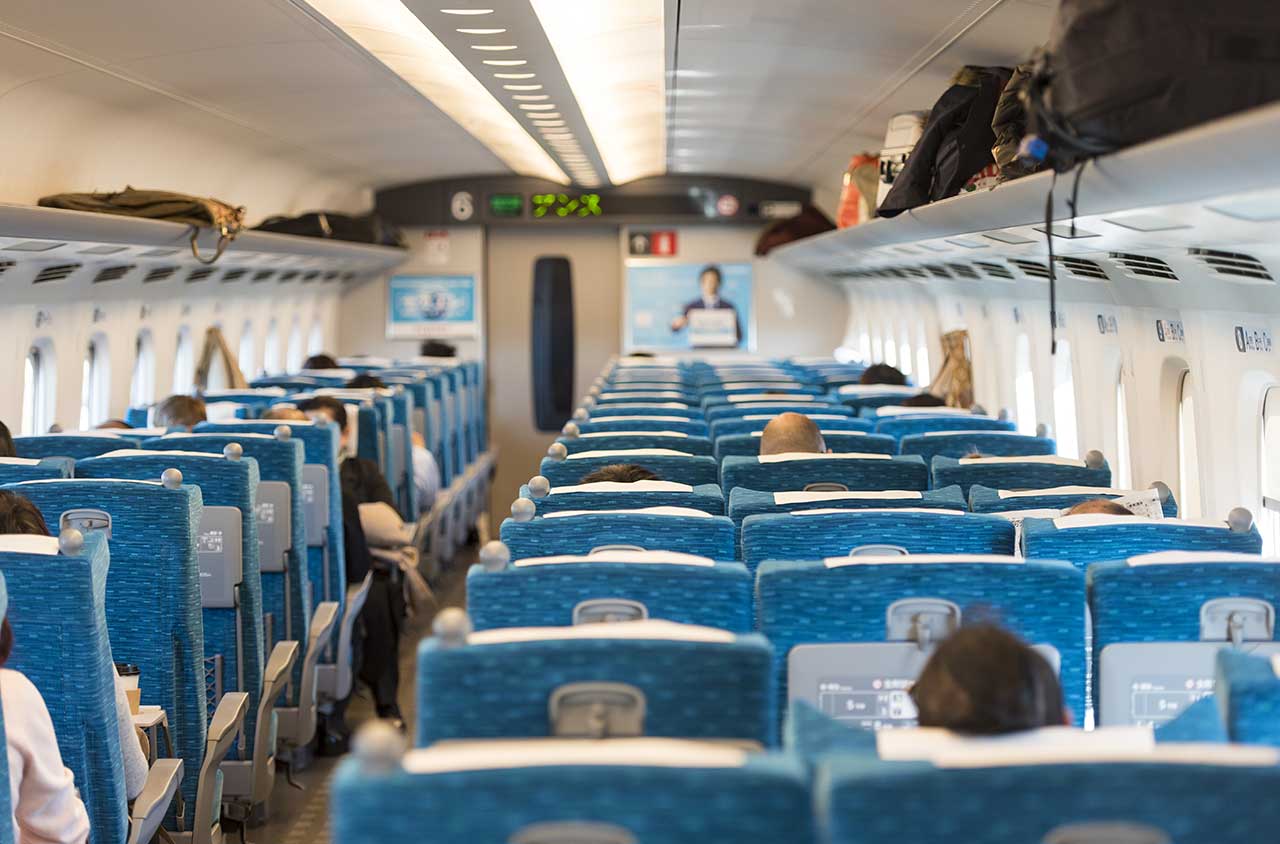

Travellers with Reserved Seat tickets are required to take their numbered seat in the Green Cars or the Ordinary Cars. Travellers with Non-reserved Seat tickets are allowed to take any seat available in the Ordinary cars designated as Non-reserved. On these cars, seating is on a first-come, first-served basis. When all the seats are full, passengers must travel standing on the corridor or the coach entrance without blocking the access to other passengers.
Limited Express conventional rail
JR Group operates many intercity and regional lines with trains running on conventional rail at a maximum speed of 130-160 km/h.
Given the limited coverage of the Shinkansen network, passengers may need to use conventional trains to reach certain regions of Japan or travel directly between two cities.

Conventional rail services are classified depending on the stop pattern:
- - Limited Express is the fastest service
- - Express is a semi-fast service stopping at major stations
- - Rapid is a fast service stopping at most stations
- - Local is a slow service stopping at all stations

When travelling on conventional rail, the standard ticket depends on the travel distance and it is the same for all the trains regardless of the number of stops or transfers. The standard ticket allows the passenger to access the platform and board Express, Rapid or Local trains. To board Limited Express trains, passengers are required an extra ticket for Reserved Seat or Non-reserved Seat, which is purchased separately from the standard ticket and is inspected by the train conductor on board.
In total, the Limited Express trains offer three passengers classes: Green Car Seat, Reserved Seat and Non-reserved Seat.
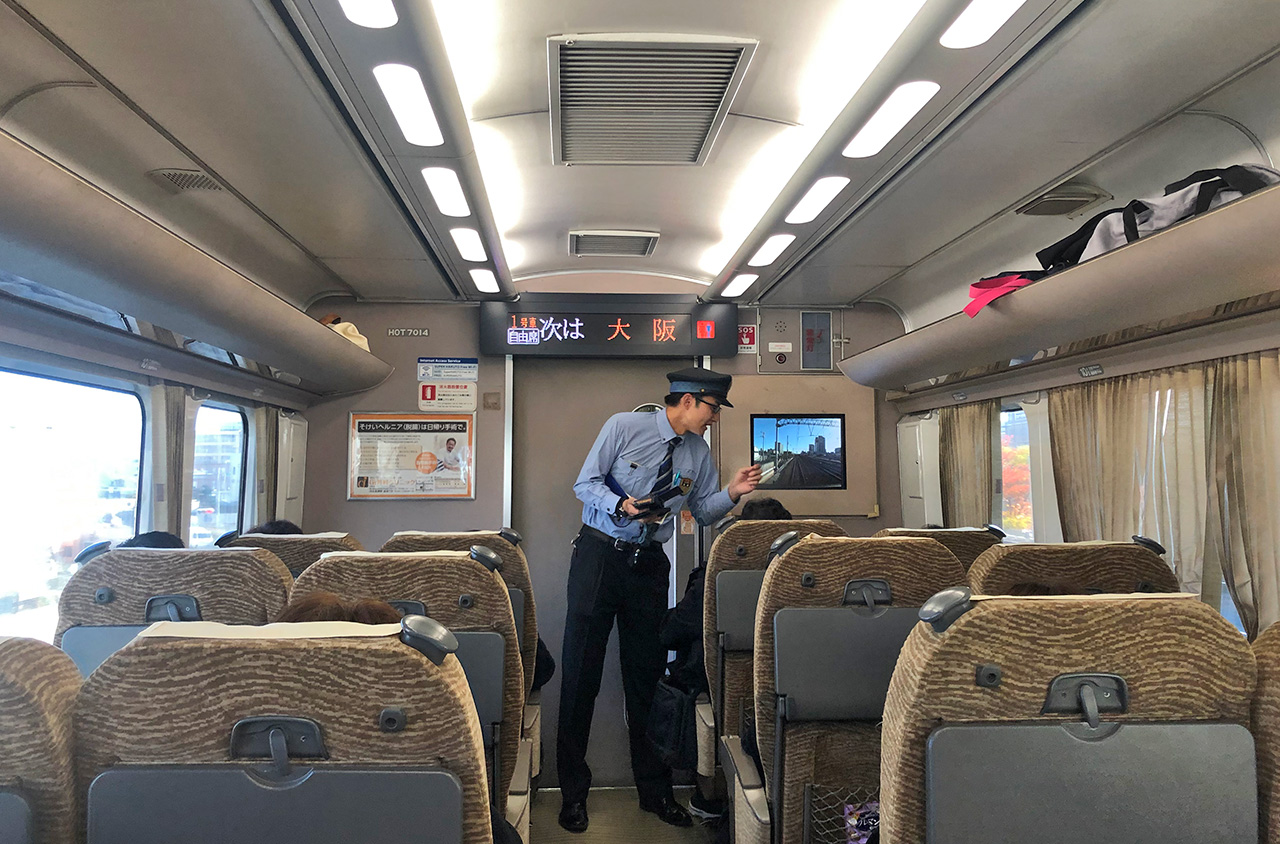

Travellers with Reserved Seat tickets are required to take their numbered seat in the Green Cars or the Ordinary Cars. Travellers with Non-reserved Seat tickets are allowed to take any seat available in the Ordinary Cars designated as Non-reserved. On these cars, seating is on a first-come, first-served basis. When all the seats are full, passengers must travel standing on the corridor or the coach entrance without blocking the access to other passengers.
Getting around Japan by train
Japan has 27,268 kilometres of railway network, which includes 2,764 kilometres of Shinkansen lines.
Travel with ticket
We facilitate advance ticket booking for Shinkansen and Limited Express trains operated by JR Hokkaido, JR East, JR Central, JR West and JR Kyushu.
Ticket reservation is available 1 month in advance.
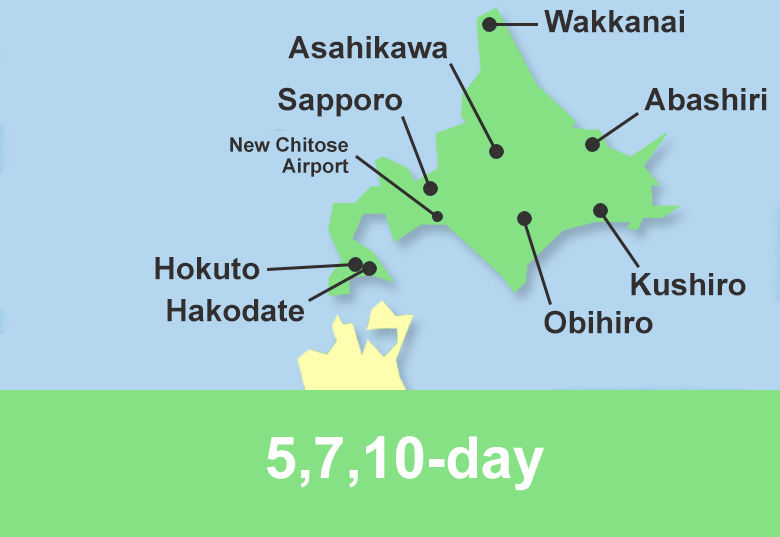
JR Hokkaido
| Stations | HAYABUSA | HAYATE |
| Shin-Aomori | ||
| Okutsugaru-Imabetsu | ||
| Kikonai | ||
| Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | HOKUTO | SUZURAN |
| Sapporo | ||
| Shin-Sapporo | ||
| Chitose | — | |
| Minami-Chitose | ||
| Numanohata | — | |
| Tomakomai | ||
| Shiraoi | — | |
| Noboribetsu | ||
| Horobetsu | — | |
| Washibetsu | — | |
| Higashi-Muroran | ||
| Datemombetsu | ||
| Toya | ||
| Oshamambe | ||
| Yakumo | ||
| Mori | ||
| Onumakoen | ||
| Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto | ||
| Goryokaku | ||
| Hakodate |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | KAMUI | LILAC | SOYA | SAROBETSU |
| Sapporo | ||||
| Iwamizawa | ||||
| Bibai | ||||
| Sunagawa | ||||
| Takikawa | ||||
| Fukagawa | ||||
| Asahikawa | ||||
| Wassamu | ||||
| Shibetsu | ||||
| Nayoro | ||||
| Bifuka | ||||
| Otoineppu | ||||
| Teshio-Nakagawa | ||||
| Horonobe | ||||
| Toyotomi | ||||
| Minami-Wakkanai | ||||
| Wakkanai |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | KAMUI | LILAC | OKHOTSK | TAISETSU |
| Sapporo | ||||
| Iwamizawa | ||||
| Bibai | ||||
| Sunagawa | ||||
| Takikawa | ||||
| Fukagawa | ||||
| Asahikawa | ||||
| Kamikawa | ||||
| Shirataki | ||||
| Maruseppu | ||||
| Engaru | ||||
| Ikutahara | ||||
| Rubeshibe | ||||
| Kitami | ||||
| Bihoro | ||||
| Memambetsu | ||||
| Abashiri |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | TOKACHI | OZORA |
| Sapporo | ||
| Shin-Sapporo | ||
| Minami-Chitose | ||
| Oiwake | ||
| Shin-Yubari | ||
| Shimukappu | ||
| Tomamu | ||
| Shintoku | ||
| Tokachi-Shimizu | ||
| Memuro | ||
| Obihiro | ||
| Ikeda | ||
| Urahoro | ||
| Shiranuka | ||
| Kushiro |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
JR East
| Stations | HAYABUSA | YAMABIKO | NASUNO | HAYATE |
| Tokyo | ||||
| Ueno | ||||
| Omiya | ||||
| Oyama | — | |||
| Utsunomiya | — | |||
| Nasushiobara | — | |||
| Shin-Shirakawa | — | |||
| Koriyama | — | |||
| Fukushima | — | |||
| Shiroishizao | — | |||
| Sendai | ||||
| Furukawa | ||||
| Kurikoma-Kogen | ||||
| Ichinoseki | ||||
| Mizusawaesashi | ||||
| Kitakami | ||||
| Shin-Hanamaki | ||||
| Morioka | ||||
| Iwate-Numakunai | ||||
| Ninohe | ||||
| Hachinohe | ||||
| Shichinohe-Towada | ||||
| Shin-Aomori |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | KOMACHI |
| Tokyo | |
| Ueno | |
| Omiya | |
| Oyama | — |
| Utsunomiya | — |
| Nasushiobara | — |
| Shin-Shirakawa | — |
| Koriyama | — |
| Fukushima | — |
| Shiroishizao | — |
| Sendai | |
| Furukawa | |
| Kurikoma-Kogen | |
| Ichinoseki | |
| Mizusawaesashi | |
| Kitakami | |
| Shin-Hanamaki | |
| Morioka | |
| Shizukuishi | |
| Tazawako | |
| Kakunodate | |
| Omagari | |
| Akita |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | TOKI | TANIGAWA |
| Tokyo | ||
| Ueno | ||
| Omiya | ||
| Kumagaya | ||
| Honjo-Waseda | ||
| Takasaki | ||
| Jomo-Kogen | ||
| Echigo-Yuzawa | ||
| Urasa | ||
| Nagaoka | ||
| Tsubamesanjo | ||
| Niigata |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | KAGAYAKI | HAKUTAKA | ASAMA | TSURUGI |
| Tokyo | ||||
| Ueno | ||||
| Omiya | ||||
| Kumagaya | — | — | ||
| Honjo-Waseda | — | — | ||
| Takasaki | — | |||
| Annaka-Haruna | — | |||
| Karuizawa | — | |||
| Sakudaira | — | |||
| Ueda | — | |||
| Nagano | ||||
| Iiyama | — | |||
| Joetsumyoko | — | |||
| Itoigawa | — | |||
| Kurobe-Unazukionsen | — | |||
| Toyama | ||||
| Shin-Takaoka | — | |||
| Kanazawa | ||||
| Komatsu 16/03/2024〜 | ||||
| Kagaonsen 16/03/2024〜 | ||||
| Awaraonsen 16/03/2024〜 | ||||
| Fukui 16/03/2024〜 | ||||
| Echizen-Takefu 16/03/2024〜 | ||||
| Tsuruga 16/03/2024〜 |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | TSUGARU | INAHO | SHIRAYUKI |
| Aomori | |||
| Akita | |||
| Niigata | |||
| Joetsu |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | NIKKO | KINUGAWA |
| Shinjuku | ||
| Ikebukuro | ||
| Omiya | ||
| Tochigi | ||
| Shimo-Imaichi | ||
| Tobu-Nikko | ||
| Kinugawa-Onsen |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | AZUSA |
| Tokyo | |
| Shinjuku | |
| Tachikawa | |
| Hachioji | |
| Otsuki | |
| Kofu | |
| Nirasaki | |
| Chino | |
| Kami-Suwa | |
| Okaya | |
| Shiojiri | |
| Matsumoto |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | SHINANO |
| Shiojiri | |
| Matsumoto | |
| Akashina | |
| Hijiri-Kogen | |
| Shinonoi | |
| Nagano |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | FUJI EXCURSION |
| Shinjuku | |
| Tachikawa | |
| Hachioji | |
| Otsuki | |
| Mt. Fuji | |
| Kawaguchiko |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
JR Central
| Stations | NOZOMI | HIKARI | KODAMA |
| Tokyo | |||
| Shinagawa | |||
| Shin-Yokohama | |||
| Odawara | — | ||
| Atami | — | ||
| Mishima | — | ||
| Shin-Fuji | — | — | |
| Shizuoka | — | ||
| Kakegawa | — | — | |
| Hamamatsu | — | ||
| Toyohashi | — | ||
| Mikawa-Anjo | — | — | |
| Nagoya | |||
| Gifu-Hashima | — | ||
| Maibara | — | ||
| Kyoto | |||
| Shin-Osaka |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
JR West
| Stations | NOZOMI | HIKARI | KODAMA | MIZUHO | SAKURA |
| Shin-Osaka | |||||
| Shin-Kobe | |||||
| Nishi-Akashi | — | — | |||
| Himeji | |||||
| Aioi | — | — | — | ||
| Okayama | |||||
| Shin-Kurashiki | — | — | — | ||
| Fukuyama | — | ||||
| Shin-Onomichi | — | — | — | ||
| Mihara | — | — | — | ||
| Higashi-Hiroshima | — | — | — | ||
| Hiroshima | |||||
| Shin-Iwakuni | — | — | — | ||
| Tokuyama | — | ||||
| Shin-Yamaguchi | — | ||||
| Asa | — | — | — | — | |
| Shin-Shimonoseki | — | — | |||
| Kokura | |||||
| Hakata |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | THUNDERBIRD |
| Osaka | |
| Shin-Osaka | |
| Takatsuki | |
| Kyoto | |
| Katata | |
| Omi-Imazu | |
| Tsuruga | |
| Takefu 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Sabae 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Fukui 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Awaraonsen 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Kagaonsen 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Komatsu 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Matto 〜15/03/2024 | |
| Kanazawa 〜15/03/2024 |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | HARUKA |
| Kansai Airport | |
| Hineno | |
| Izumi-Fuchu | |
| Tennoji | |
| Osaka | |
| Shin-Osaka | |
| Takatsuki | |
| Kyoto |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
JR Kyushu
| Stations | MIZUHO | SAKURA | TSUBAME |
| Hakata | |||
| Shin-Tosu | — | ||
| Kurume | — | ||
| Chikugo-Funagoya | — | — | |
| Shin-Omuta | — | — | |
| Shin-Tamana | — | — | |
| Kumamoto | |||
| Shin-Yatsushiro | — | ||
| Shin-Minamata | — | ||
| Izumi | — | ||
| Sendai | |||
| Kagoshima-Chuo |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Travel with tourist pass
We also facilitate the purchase of different tourist pass with JR West as well as the private railway companies Hanshin Railway, Hankyu Railway and Kintetsu Railway.
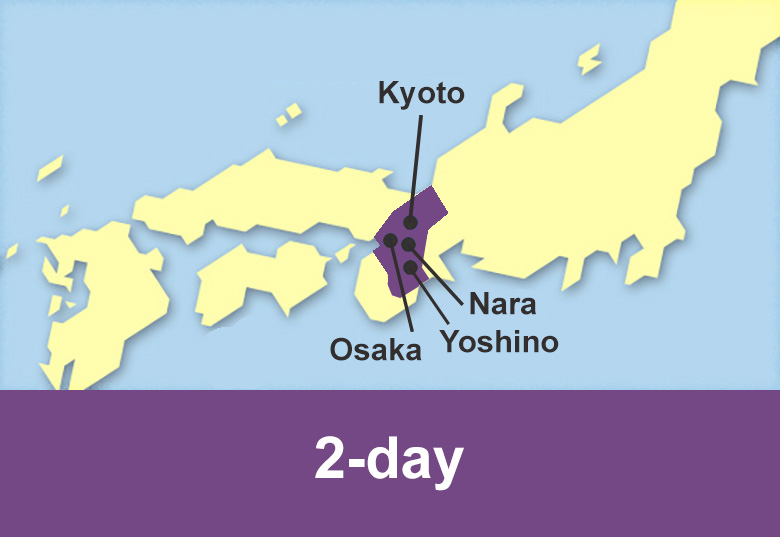
Passengers can travel on Express, Rapid or Local trains for 1 or 2 days.
Tourist pass reservation is available 3 months in advance.
JR West
| Stations | Miyakoji Rapid | Rapid | Regional Rapid |
| Kyoto | |||
| Tofukuji | |||
| Inari | — | — | |
| Rokujizo | |||
| Uji | |||
| Ogura | — | ||
| Shinden | — | ||
| Joyo | |||
| Nagaike | — | — | |
| Yamashiro-Aodani | — | — | |
| Yamashiro-Taga | — | — | |
| Tamamizu | |||
| Tanakura | — | — | |
| Kamikoma | — | — | |
| Kizu | |||
| Narayama | — | — | |
| Nara |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Yamatoji Rapid | Rapid | Direct Rapid | Regional Rapid |
| Osaka | ||||
| Namba | ||||
| Imamiya | — | — | ||
| Shin-Imamiya | ||||
| Tennoji | ||||
| Kyuhoji | ||||
| Oji | ||||
| Horyuji | ||||
| Yamato-Koizumi | ||||
| Koriyama | ||||
| Nara | ||||
| Narayama | ||||
| Kizu | ||||
| Kamo |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Special Rapid | Rapid |
| Osaka | ||
| Amagasaki | ||
| Nishinomiya | — | |
| Ashiya | ||
| Sumiyoshi | — | |
| Rokkomichi | — | |
| Sannomiya | ||
| Motomachi | — | |
| Kobe | ||
| Hyogo | — | |
| Akashi | ||
| Nishi-Akashi | ||
| Kakogawa | ||
| Himeji |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Hanshin Railway
| Stations | Limited Express | Rapid Express |
| Kobe-Sannomiya | ||
| Amagasaki | ||
| Osaka-Umeda | ||
| Osaka-Namba |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Hankyu Railway
| Stations | Limited Express | Local + Limited Express |
| Kyoto-Arashiyama | ||
| Kyoto-Kawaramachi | ||
| Katsura | ||
| Juso | ||
| Osaka-Umeda |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express |
| Kobe-Sannomiya | |
| Juso | |
| Osaka-Umeda |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Kintetsu Railway
| Stations | Limited Express | Rapid Express |
| Osaka-Namba | ||
| Kintetsu Nippombashi | ||
| Osaka Uehommachi | ||
| Tsuruhashi | — | |
| Ikoma | ||
| Gakuen-mae | ||
| Yamato-Saidaiji | ||
| Shin-Omiya | — | |
| Kintetsu-Nara |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Kyoto | ||
| Toji | — | |
| Takeda | — | |
| Kintetsu-Tambabashi | ||
| Momoyamagoryomae | — | |
| Okubo | — | |
| Shin-Tanabe | — | |
| Shin-Hosono | ||
| Takanohara | ||
| Yamato-Saidaiji | ||
| Shin-Omiya | — | |
| Kintetsu-Nara |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Kyoto | ||
| Toji | — | |
| Takeda | — | |
| Kintetsu-Tambabashi | ||
| Momoyamagoryomae | — | |
| Okubo | — | |
| Shin-Tanabe | — | |
| Shin-Hosono | ||
| Takanohara | ||
| Yamato-Saidaiji | ||
| Nishinokyo | ||
| Kintetsu-Koriyama | — | |
| Hirahata | — | |
| Tawaramoto | — | |
| Yamato-Yagi | ||
| Yagi-nishiguchi | ||
| Unebigoryomae | — | |
| Kashiharajingu-mae | ||
| Okadera | — | |
| Asuka | ||
| Tsubosakayama | ||
| Ichio | — | |
| Kuzu | — | |
| Yoshinoguchi | ||
| Kusurimizu | — | |
| Fukugami | ||
| Oada | — | |
| Shimoichiguchi | ||
| Koshibe | — | |
| Muda | ||
| Yamato-Kamiichi | ||
| Yoshino-Jingu | ||
| Yoshino |
Interchange trains, All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Osaka-Abenobashi | ||
| Furuichi | ||
| Shakudo | ||
| Takadashi | ||
| Kashiharajingu-mae | ||
| Okadera | — | |
| Asuka | ||
| Tsubosakayama | ||
| Ichio | — | |
| Kuzu | — | |
| Yoshinoguchi | ||
| Kusurimizu | — | |
| Fukugami | ||
| Oada | — | |
| Shimoichiguchi | ||
| Koshibe | — | |
| Muda | ||
| Yamato-Kamiichi | ||
| Yoshino-Jingu | ||
| Yoshino |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Osaka-Namba | ||
| Kintetsu Nippombashi | ||
| Osaka Uehommachi | ||
| Tsuruhashi | ||
| Fuse | ||
| Kawachi-Kokubu | — | |
| Goido | — | |
| Yamato-Takada | ||
| Yamato-Yagi | ||
| Sakurai | — | |
| Haibara | ||
| Muroguchi-Ono | — | |
| Akameguchi | — | |
| Nabari | ||
| Kikyogaoka | ||
| Iga-Kambe | ||
| Sakakibara-Onsenguchi | ||
| Ise-Nakagawa | ||
| Momozono | — | |
| Hisai | ||
| Minamigaoka | — | |
| Tsu-shimmachi | — | |
| Tsu | ||
| Edobashi | — | |
| Shiroko | ||
| Ise-Wakamatsu | — | |
| Shiohama | — | |
| Kintetsu-Yokkaichi | ||
| Kintetsu-Tomida | — | |
| Kuwana | ||
| Kintetsu-Yatomi | — | |
| Kintetsu-Kanie | — | |
| Kintetsu-Nagoya |
Interchange trains, All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Osaka-Namba | ||
| Kintetsu Nippombashi | ||
| Osaka Uehommachi | ||
| Tsuruhashi | ||
| Fuse | ||
| Kawachi-Kokubu | — | |
| Goido | — | |
| Yamato-Takada | ||
| Yamato-Yagi | ||
| Sakurai | — | |
| Haibara | ||
| Muroguchi-Ono | — | |
| Akameguchi | — | |
| Nabari | ||
| Kikyogaoka | ||
| Iga-Kambe | ||
| Sakakibara-Onsenguchi | ||
| Ise-Nakagawa | ||
| Matsusaka | ||
| Iseshi | ||
| Ujiyamada |
Interchange trains, All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Limited Express | Express |
| Kintetsu-Nagoya | ||
| Kintetsu-Kanie | — | |
| Kintetsu-Yatomi | — | |
| Kuwana | ||
| Kintetsu-Tomida | — | |
| Kintetsu-Yokkaichi | ||
| Shiohama | — | |
| Ise-Wakamatsu | — | |
| Shiroko | ||
| Edobashi | — | |
| Tsu | ||
| Tsu-shimmachi | — | |
| Minamigaoka | — | |
| Hisai | ||
| Momozono | — | |
| Ise-Nakagawa | ||
| Matsusaka | ||
| Iseshi | ||
| Ujiyamada |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
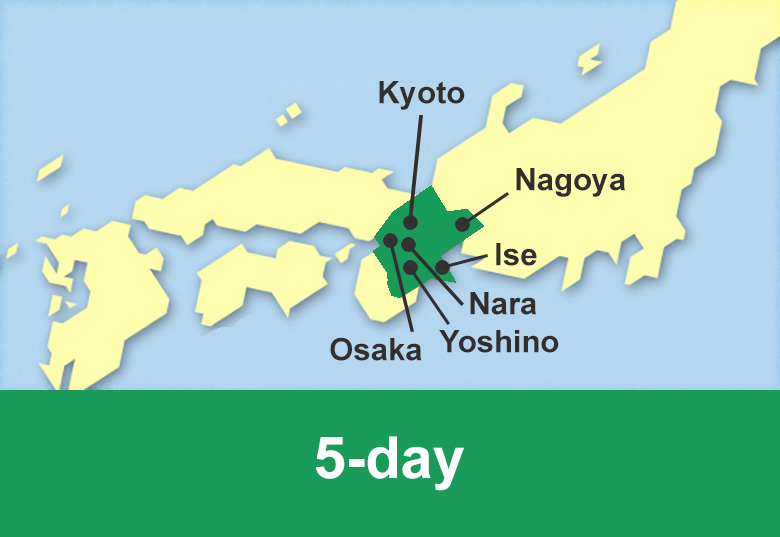
Travel with rail pass
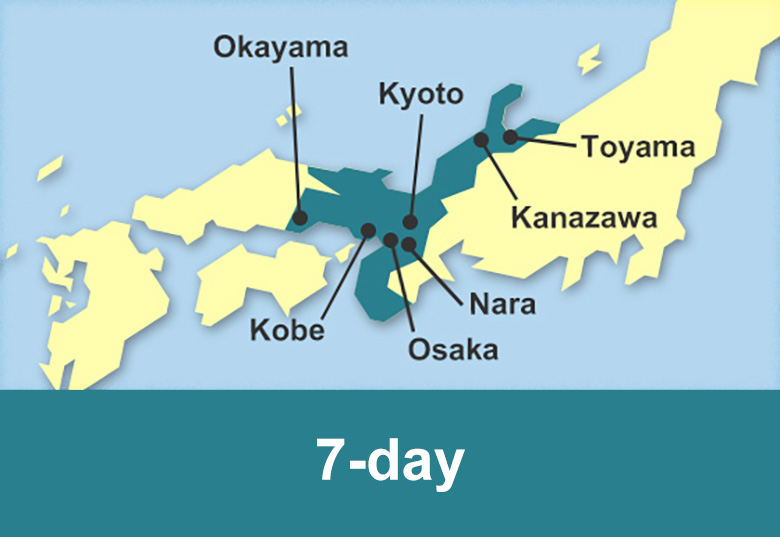
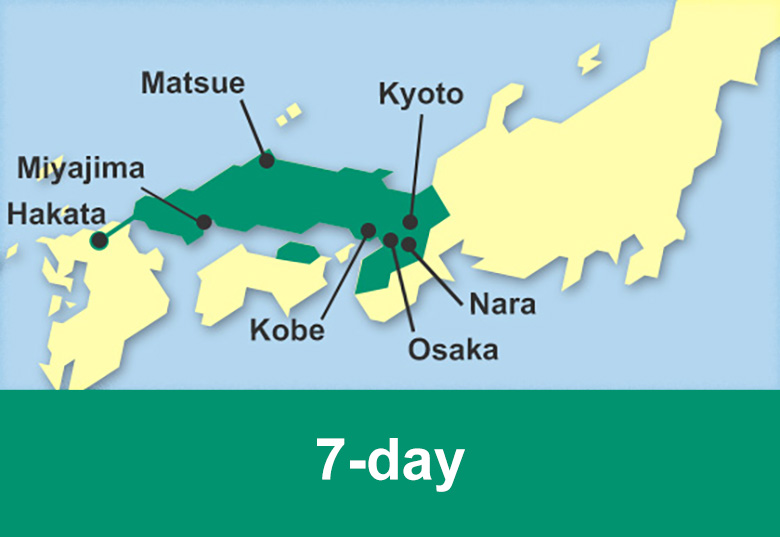
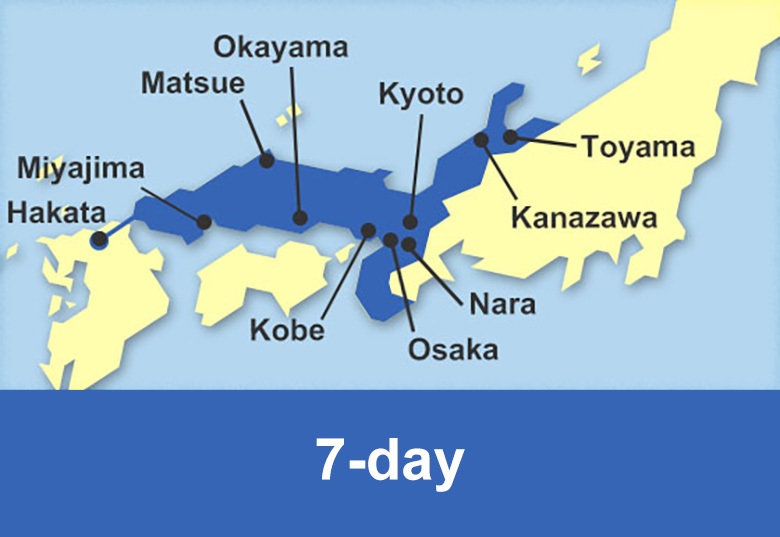
We facilitate the purchase of different rail pass with JR Hokkaido, JR East and JR West as well as the private railway company Kintetsu Railway valid for unlimited travel in Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai and Chugoku regions and Fukuoka prefecture in Kyushu island.
Passengers can travel on Shinkansen trains, Limited Express trains, as well as Express, Rapid or Local trains in the available area for a number of consecutive days.
Rail pass reservation is available 3 months in advance.
Destinations
Japan is divided into eight regions: Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku and Kyushu.
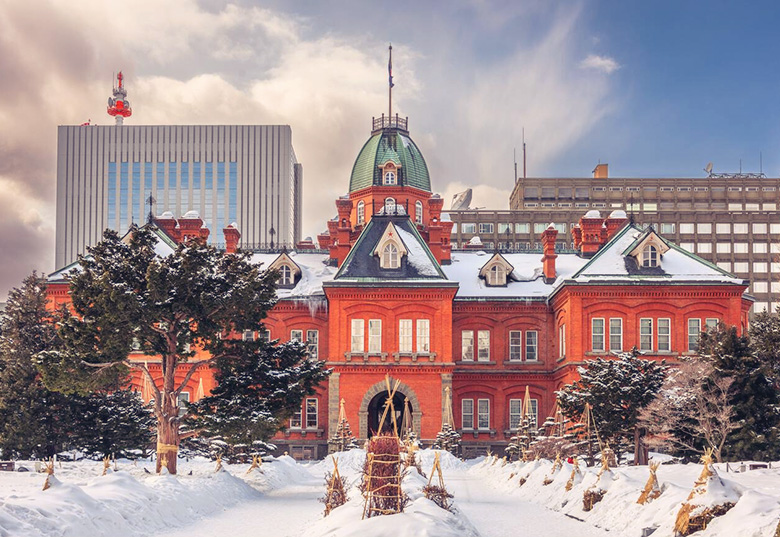
Hokkaido island
Hokkaido is the second largest island of Japan and comprises only one prefecture, Hokkaido, whose capital is Sapporo. This region is served by the Hokkaido Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR Hokkaido.
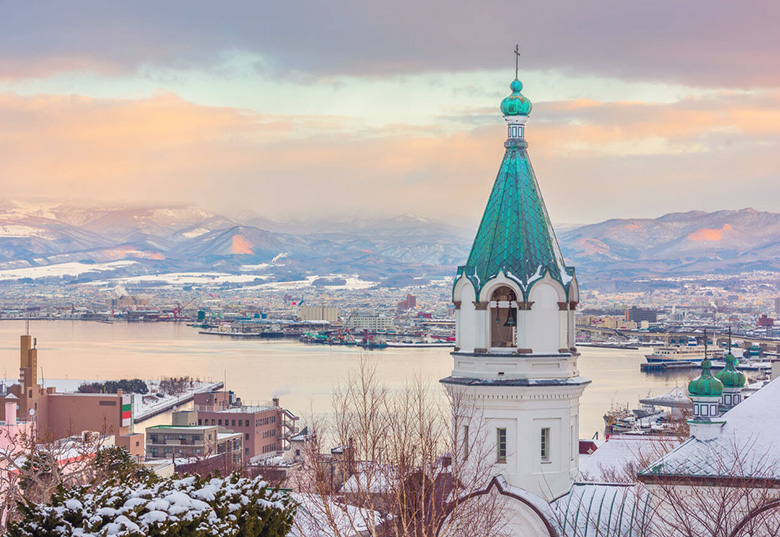


Train routes to Hakodate
Tohoku region
Tohoku region comprises Aomori, Akita, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi and Yamagata prefectures. This region is served by the Tohoku Shinkansen, the Akita Shinkansen, the Yamagata Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR East.

Train routes to Aomori

Train routes to Hirosaki

Train routes to Akita

Train routes to Sendai
Kanto region
Kanto region comprises Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa prefectures. This region is served by the Tohoku Shinkansen, the Tokaido Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR East.

Train routes to Tokyo

Train routes to Nikko
Chubu region
Chubu region comprises Yamanashi, Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu, Fukui, Ishikawa, Toyama, Nagano and Niigata prefectures. This region is served by the Tokaido Shinkansen, the Hokuriku Shinkansen, the Joetsu Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR East, JR Central and JR West.

Train routes to Fuji

Train routes to Shizuoka

Train routes to Nagoya

Train routes to Matsumoto

Train routes to Nagano

Train routes to Niigata

Train routes to Kanazawa
Kansai region
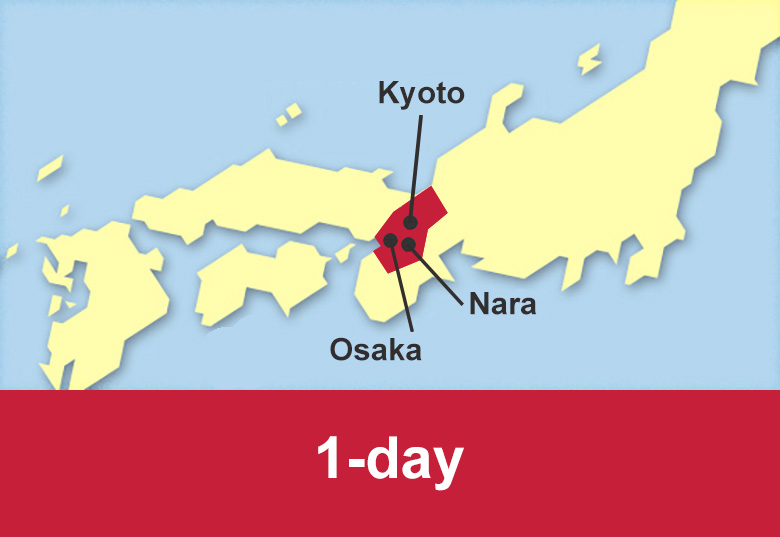
Kansai region comprises Mie, Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyogo and Shiga prefectures. This region is served by the Tokaido Shinkansen, the Sanyo Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR Central, JR West, Hanshin Railway, Hankyu Railway and Kintetsu Railway.
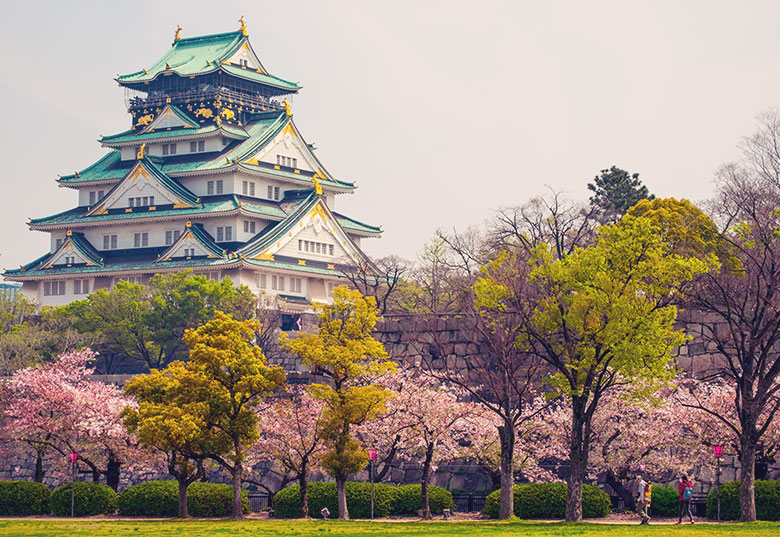
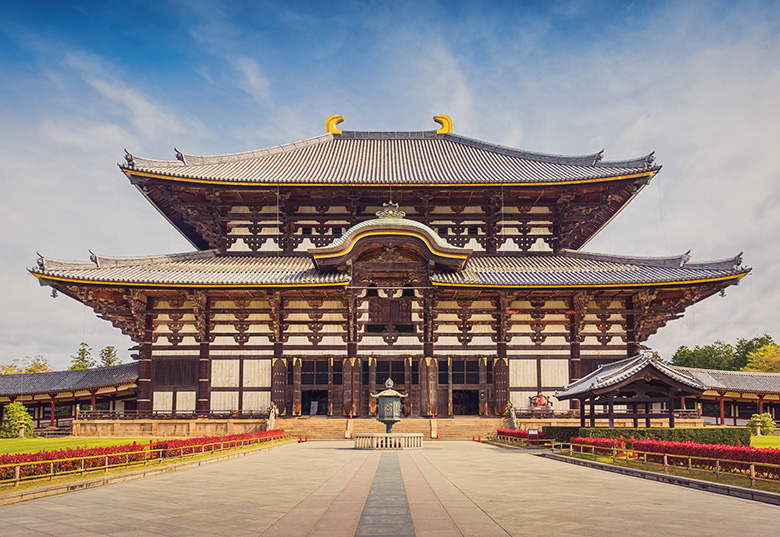



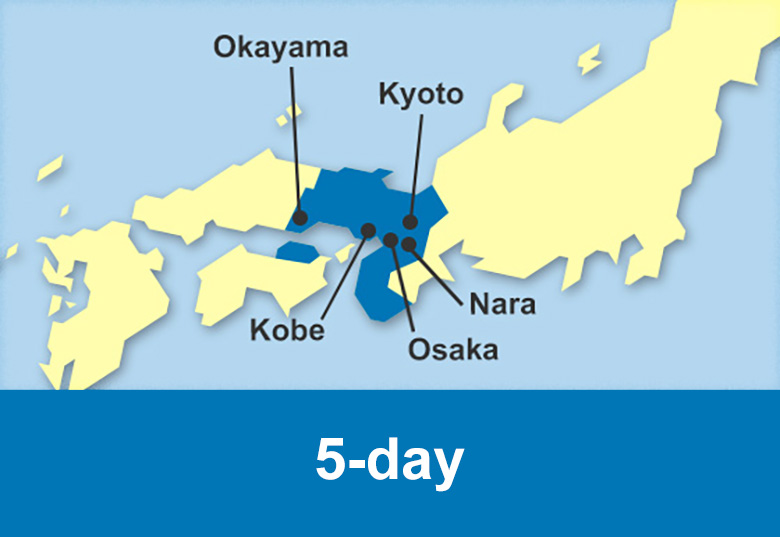
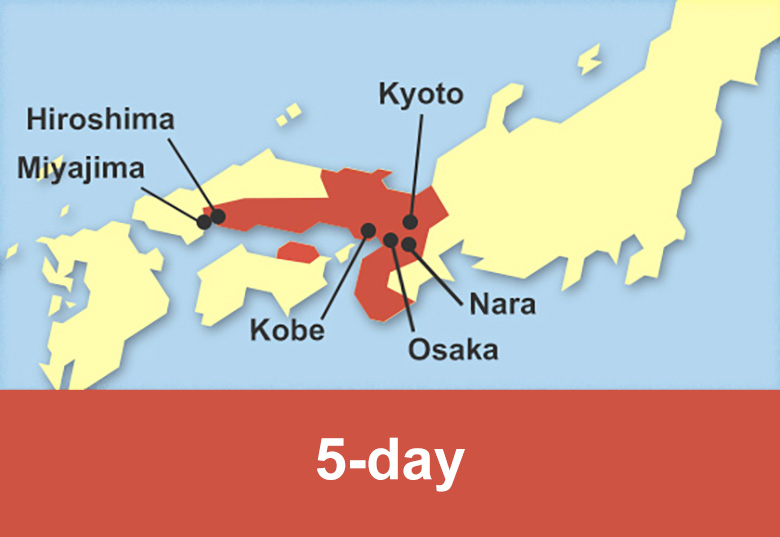
Train routes to Nara
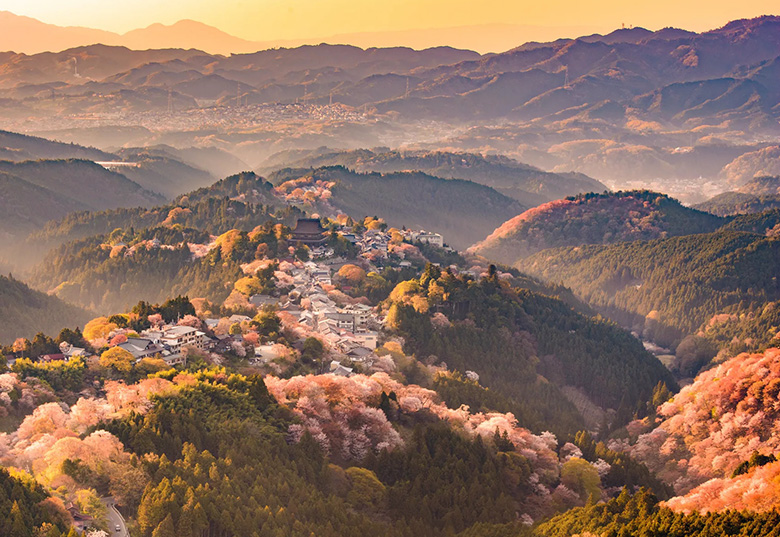

Train routes to Yoshino
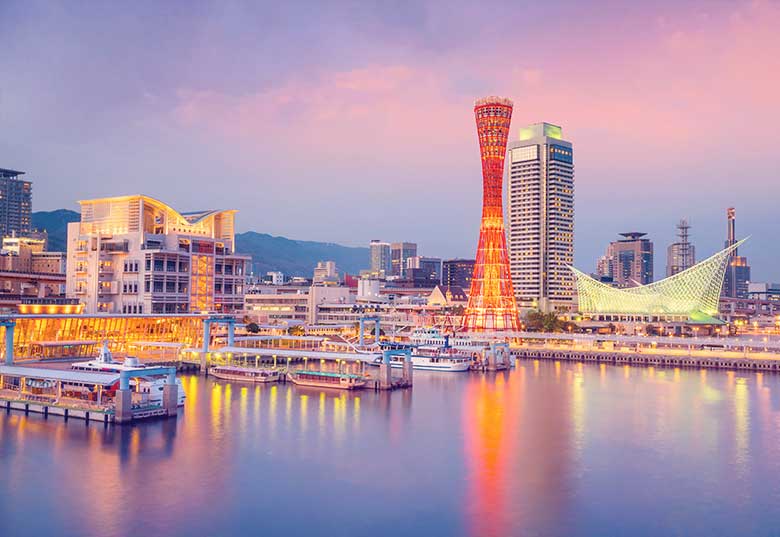

Train routes to Kobe
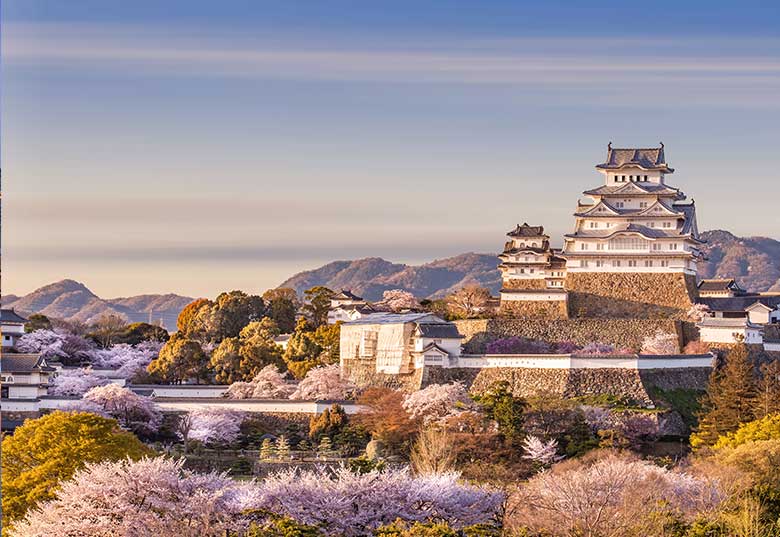

Train routes to Himeji
Chugoku region
Chugoku region comprises Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi, Shimane and Tottori prefectures. This region is served by the Sanyo Shinkansen and the Limited Express trains operated by JR West.
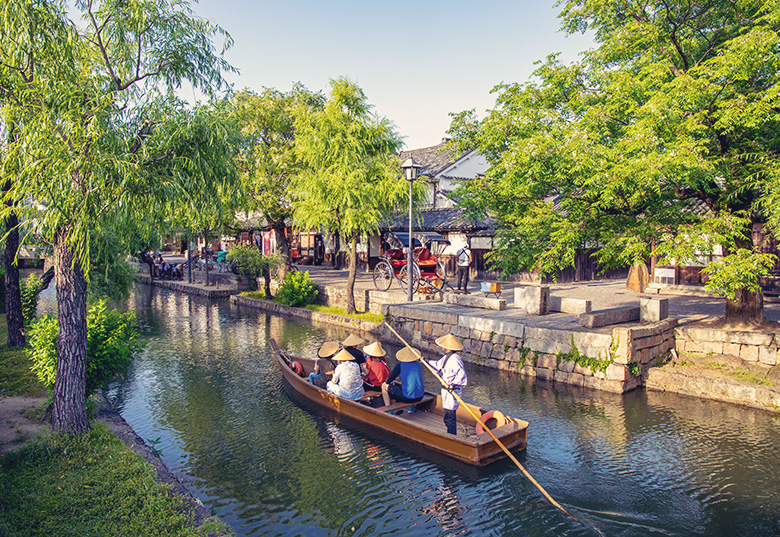

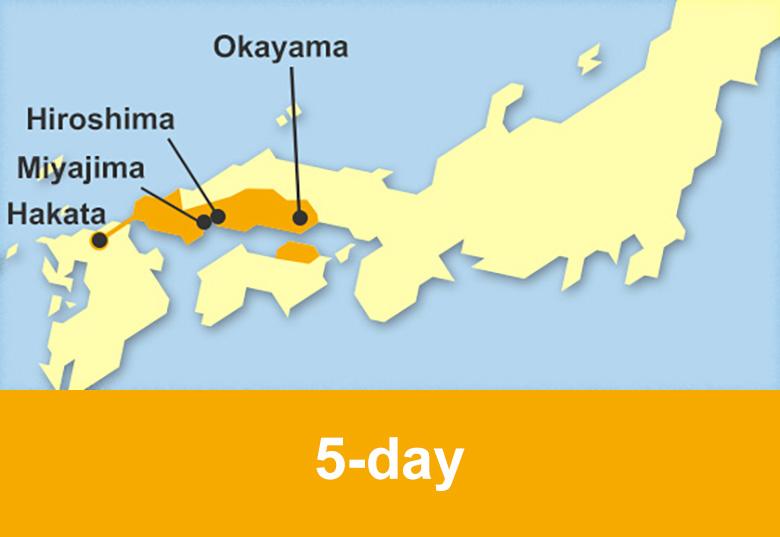
Train routes to Okayama
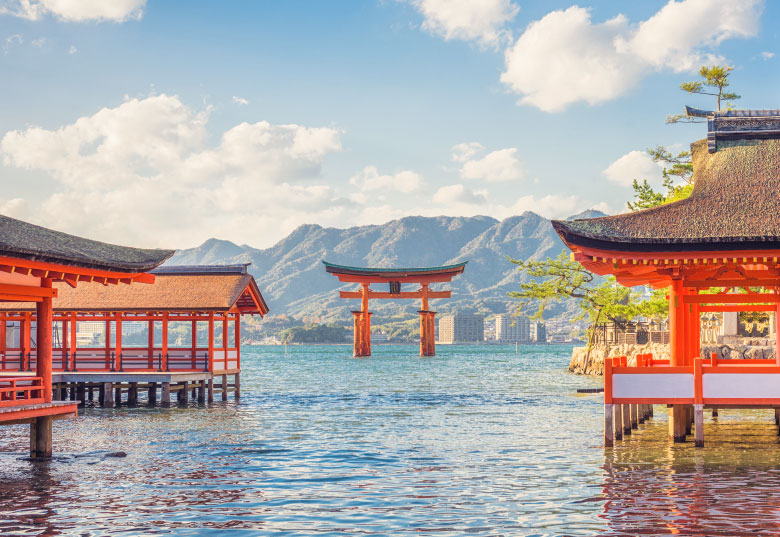

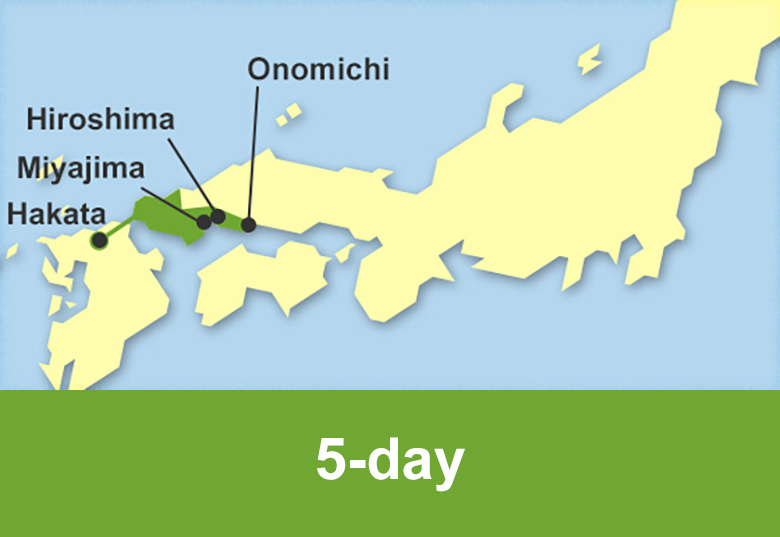
Train routes to Hiroshima
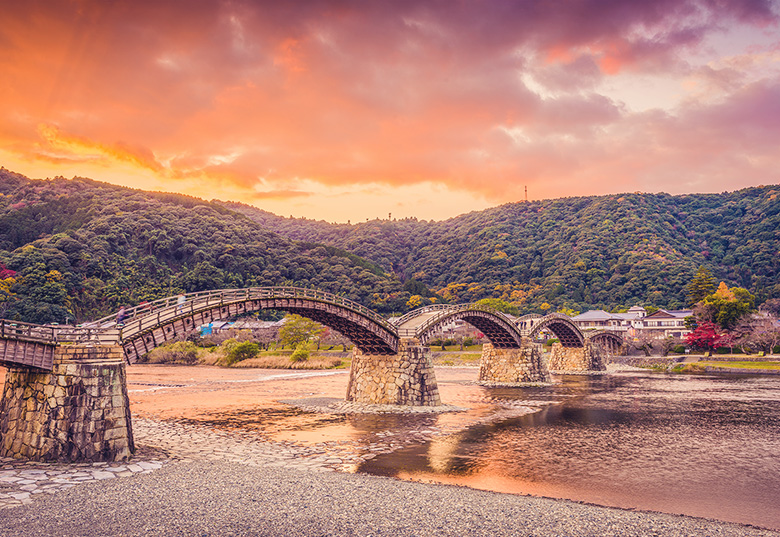

Train routes to Yamaguchi
Kyushu island
Kyushu is the third largest of Japan's five main islands. This region is served by the Sanyo Shinkansen and the Kyushu Shinkansen.
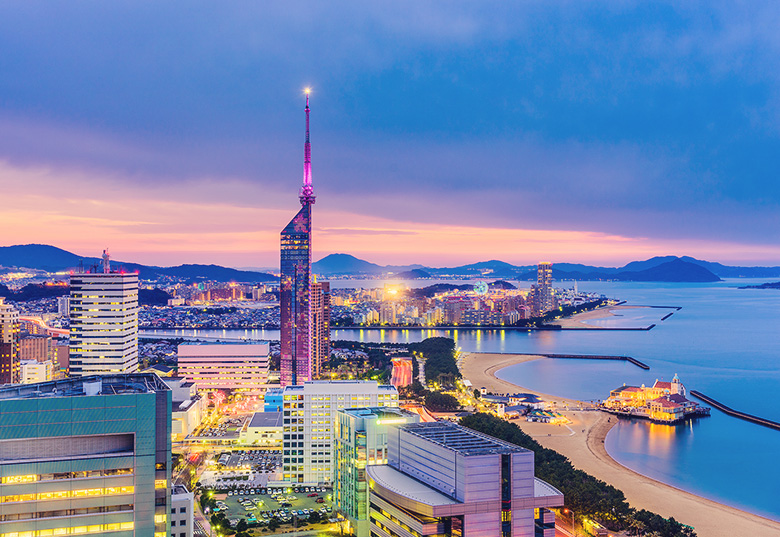

Train routes to Fukuoka
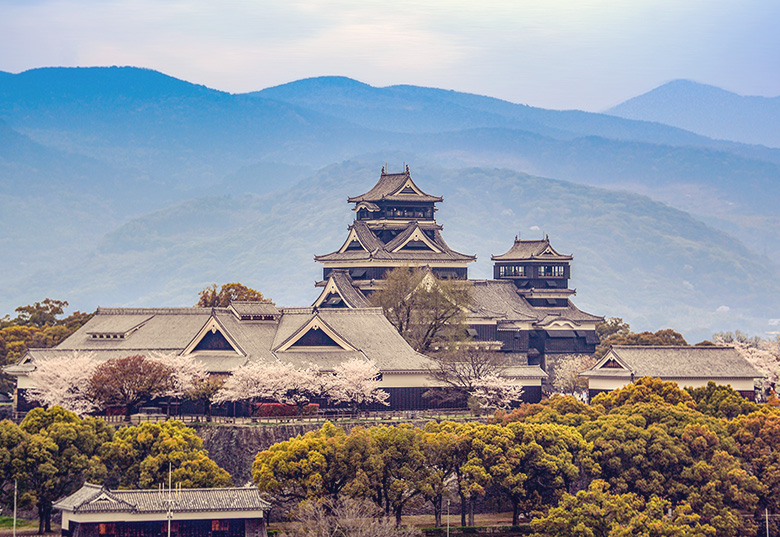

Train routes to Kumamoto
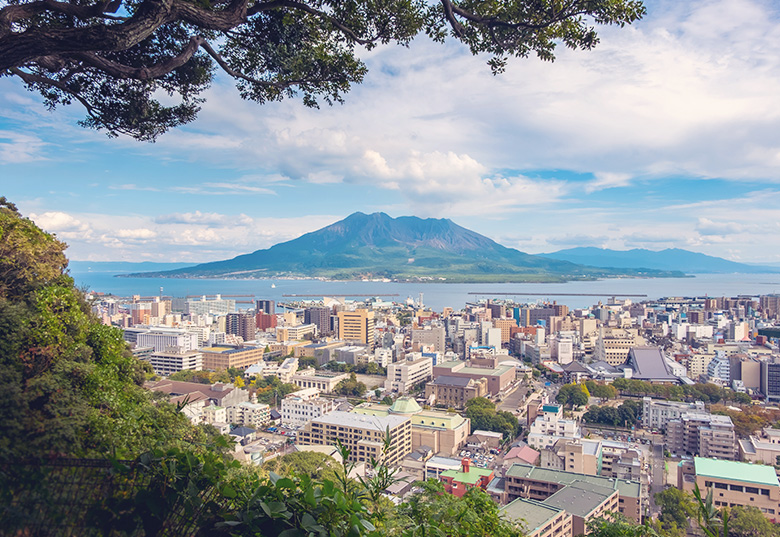

Train routes to Kagoshima
Getting around Tokyo by train and subway
Tokyo's urban rail network comprises train lines operated by Japan Railways (JR) and subway lines operated by Tokyo Metro and Toei Subway.
Getting around Tokyo with rail pass
The railway company JR East operates two train lines that interconnect Tokyo's major stations, including Tokyo, Akibahara, Ueno, Ikebukuro, Shinjuku and Shibuya.
Travellers with Japan Rail Pass or JR East Pass can get around Tokyo using the Yamanote Line and the Chuo-Sobu Line since the services are operated by JR East.
JR East
| Stations | Local | Tokyo |
| Shinagawa | |
| Shibuya | |
| Shinjuku | |
| Ikebukuro | |
| Ueno | |
| Akihabara | |
| Tokyo |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Rapid | Local |
| Shinjuku | ||
| Akihabara | — | |
| Tokyo | — |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Getting around Tokyo with subway pass
Tokyo Metro interconnects Tokyo's major stations, including Tokyo, Akibahara, Ueno, Ikebukuro, Shinjuku and Shibuya, so the subway network in an alternative way to get around the city.
Travellers who want to get around Tokyo using the Tokyo Metro services can purchase the Tokyo Subway Ticket. This ticket is valid for unlimited rides during 24-hours, 48-hours and 72-hours.
Tokyo Metro
| Stations | GINZA | Tokyo | — |
| Shinagawa | — |
| Shibuya | |
| Shinjuku | — |
| Ikebukuro | — |
| Ueno | |
| Asakusa | |
| Akihabara | — |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | MARUNOUCHI | Tokyo |
| Shinagawa | — |
| Shibuya | — |
| Shinjuku | |
| Ikebukuro | |
| Ueno | — |
| Asakusa | — |
| Akihabara | — |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | HIBIYA | Tokyo | — |
| Shinagawa | — |
| Shibuya | — |
| Shinjuku | — |
| Ikebukuro | — |
| Ueno | |
| Asakusa | — |
| Akihabara |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | FUKUTOSHIN | Tokyo | — |
| Shinagawa | — |
| Shibuya | |
| Shinjuku | — |
| Ikebukuro | |
| Ueno | — |
| Asakusa | — |
| Akihabara | — |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop

Train and subway routes in Tokyo
Getting to Tokyo Airport by train
Narita Airport is connected to Tokyo, Shinagawa, Shinjuku and Ueno stations in Tokyo by the Limited Express trains operated by JR East and Keisei Railway.
Travellers with Japan Rail Pass or JR East Pass can reserve seats on the Narita Express since the service is operated by JR East. Other travellers can book tickets 1 month in advance.
JR East
| Stations | NARITA |
| Narita Airport | |
| Narita | |
| Yotsukaido | |
| Chiba | |
| Tokyo | |
| Shinagawa | |
| Shinjuku |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Keisei Railway
| Stations | SKYLINER |
| Narita Airport | |
| Shin-Kamagaya | |
| Aoto | |
| Nippori | |
| Keisei Ueno |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
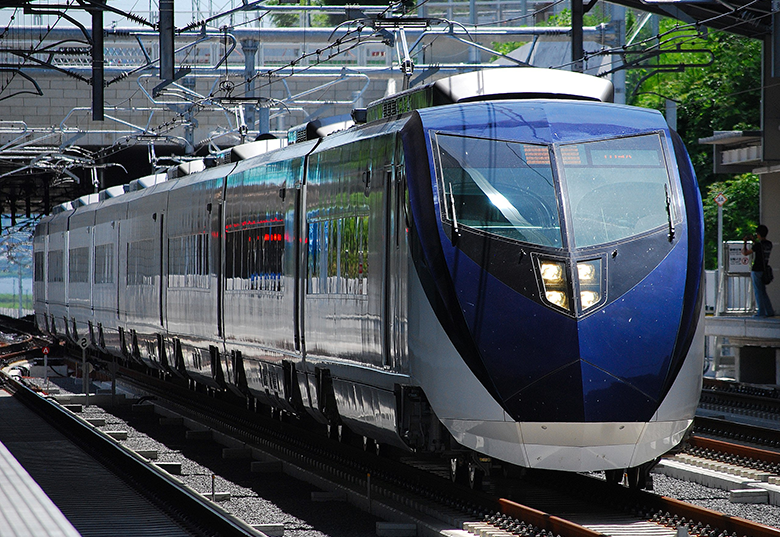

Train routes to Narita Airport
Getting around Osaka by train and subway
Osaka's urban rail network comprises train lines operated by Japan Railways (JR) and subway lines operated by Osaka Metro.
Getting around Osaka with rail pass
The railway company JR West operates two train lines that interconnect Osaka's major stations, including Osaka, Namba and Tennoji.
Travellers with the Japan Rail Pass or JR West Pass can get around Osaka using the Osaka Loop Line and the Yamatoji Line since the services are operated by JR West.
JR West
| Stations | Rapid | Local |
| Osaka | ||
| Namba | ||
| Tennoji |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
| Stations | Rapid | Local |
| Osaka | ||
| Namba | ||
| Tennoji |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Getting around Osaka with subway pass
Osaka Metro interconnects Osaka's major stations, including Shin-Osaka, Umeda, Namba and Tennoji, so the subway network in an alternative way to get around the city.
Travellers who want to get around Osaka using the Osaka Metro services can purchase the Osaka Metro Pass. This ticket is valid for unlimited rides during 1-day and 2-days.
Osaka Metro
| Stations | MIDOSUJI |
| Shin-Osaka | |
| Umeda | |
| Osaka | — |
| Namba | |
| Tennoji |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
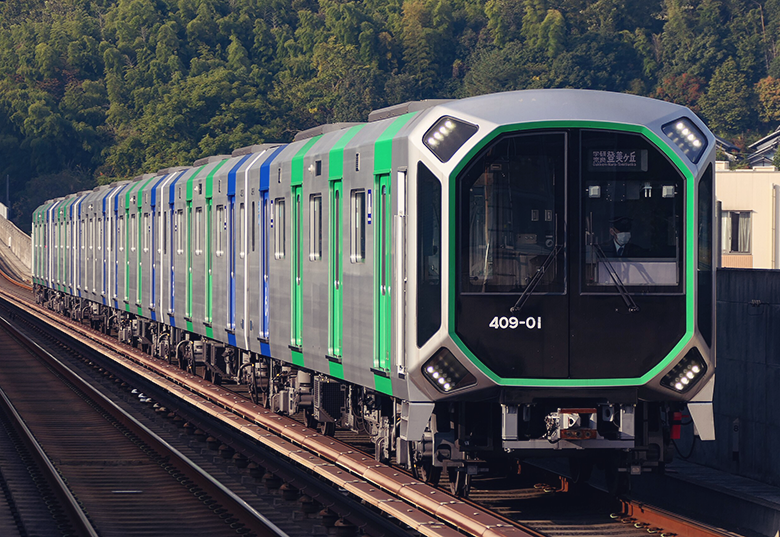

Train and subway routes in Osaka
Getting to Osaka Airport by train
Kansai Airport is connected to Shin-Osaka, Osaka, Tennoji and Namba stations in Osaka by the Limited Express trains operated by JR West and Nankai Railway.
Travellers with Japan Rail Pass or JR West Pass can reserve seats on the Haruka Express since the service is operated by JR West. Other travellers can book tickets 3 months in advance.
JR West
| Stations | HARUKA |
| Kansai Airport | |
| Hineno | |
| Izumi-Fuchu | |
| Tennoji | |
| Osaka | |
| Shin-Osaka | |
| Takatsuki | |
| Kyoto |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
Nankai Railway
| Stations | RAPI:T |
| Kansai Airport | |
| Rinku Town | |
| Izumisano | |
| Kishiwada | |
| Sakai | |
| Tengachaya | |
| Shin-Imamiya | |
| Namba |
All trains stop, Some trains stop, — Trains do not stop
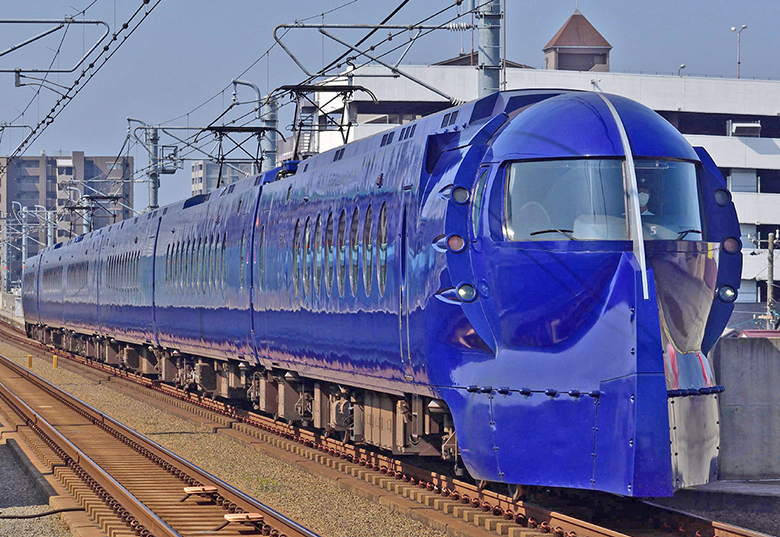

Train routes to Kansai Airport
How to book your train tickets in Japan?
Booking your train tickets in Japan is very quick and simple. Search for train routes between any two cities for your travel dates.
Select your route
After search, we will display the results for your itinerary.
Find the Shinkansen and Limited Express services operated by Japan Railways (JR) available for your itinerary. Select the most convenient option.
We accept ticket reservations from 1 month in advance up to 24 hours before departure. For departures under 24 hours, tickets must be reserved directly at the station.
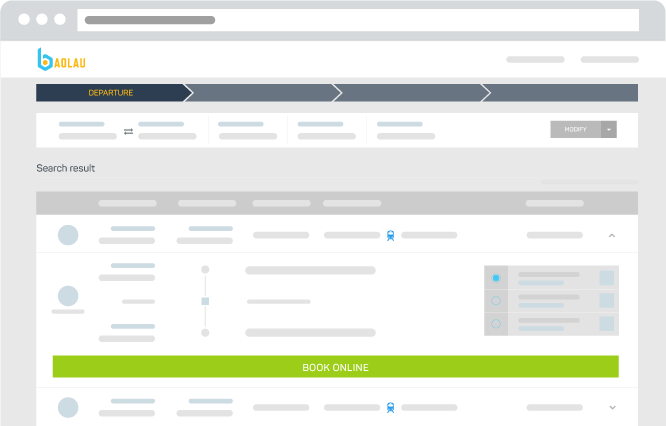
Click to expand the details of the route, you will find the available fares.
Japan Railways (JR) offers various types of fares for Shinkansen and Limited Express trains:
- Non-reserved Seat, does not require seat selection
- Reserved Seat, arranged in 3+2 row configuration
- Green Car Seat, arranged in 2+2 row configuration
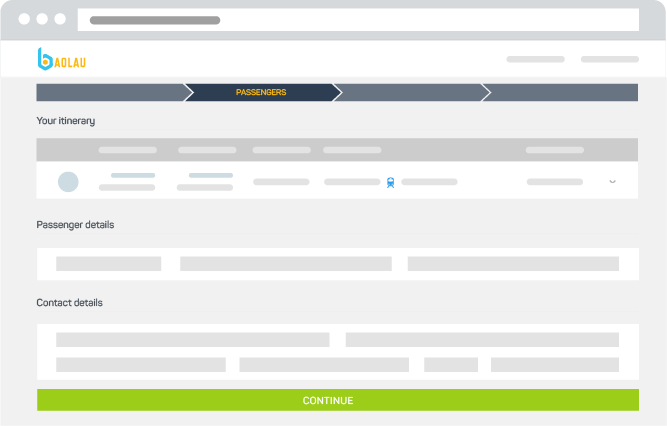
Fill in the passenger and contact details
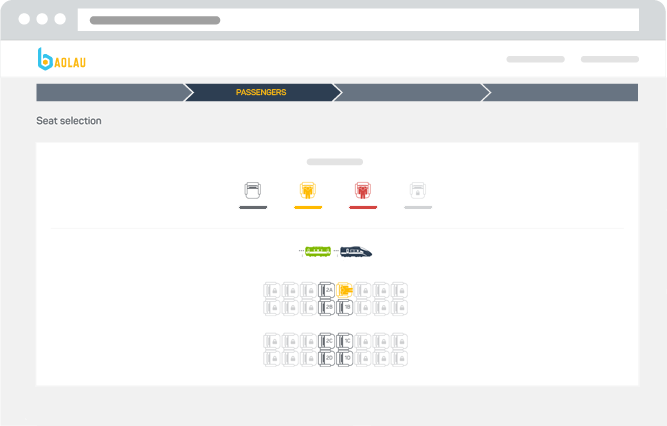
When you book train tickets, you can indicate your seat preference: window or aisle.
Passengers who intend to bring baggage with overall dimensions (length + width + height) of more than 160cm onto the Tokaido-Sanyo-Kyushu Shinkansen need to reserve a seat with Oversized Baggage Area.
Please provide the passenger information and the contact details of the person responsible for booking. We will send by email the booking confirmation and the electronic ticket.
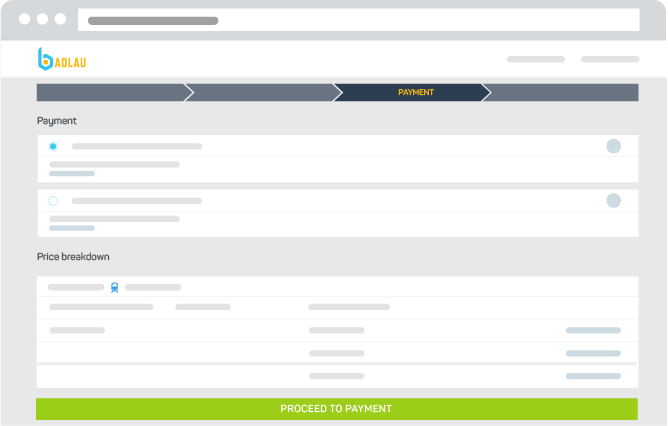
Complete your payment
Select your payment method. We accept international credit or debit cards.
Check your itinerary and price breakdown. Confirm that the booking information is correct. Before you proceed to payment, you must read and accept the terms and conditions of booking.
Receive your electronic ticket by email
Once your payment is complete, your reservation will be processed.
In the following 24 hours you will receive the itinerary and booking confirmation by email with the electronic ticket attached in PDF format.
You can also access to Manage your booking via web and download the electronic ticket to your device.
How to use the train e-ticket?
The electronic ticket designated as QR-Ticket is a valid boarding pass and can be used to board the train at the station of departure.
The electronic ticket with QR Pickup code can be used to pick up the physical ticket at the station before departure.
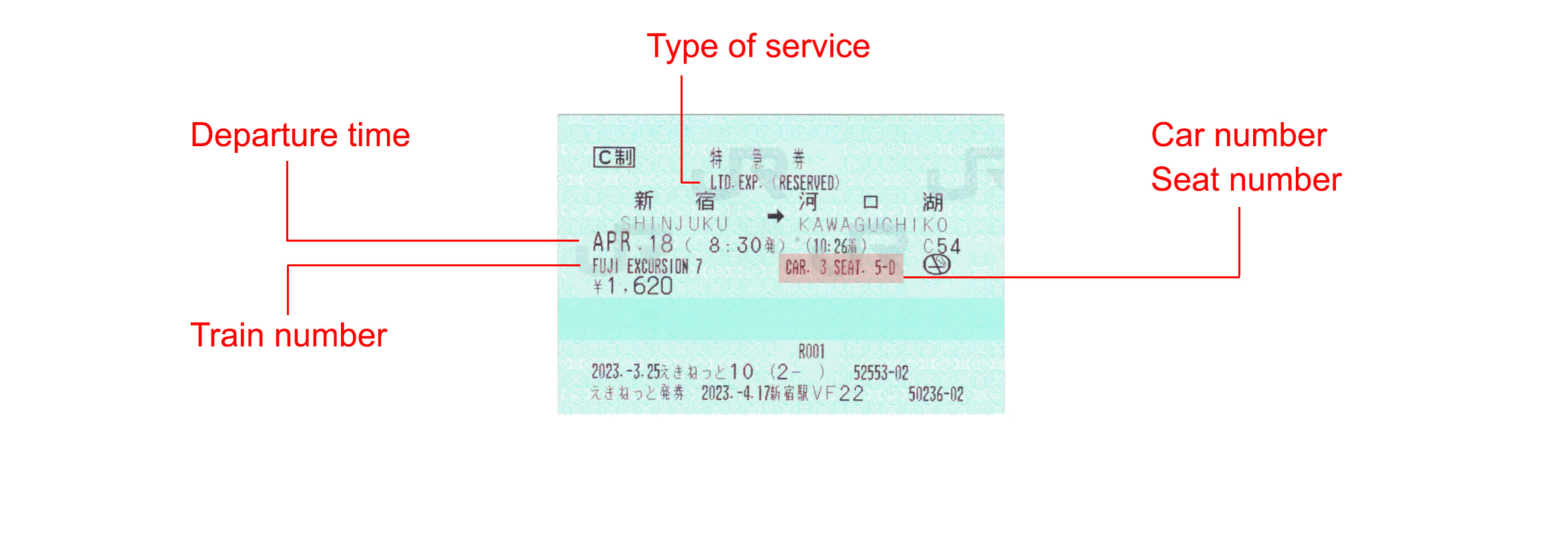
Passengers travelling with Japan Railways (JR) can print the e-ticket in advance or carry a digital copy in the mobile phone to scan the QR code at the ticket gates or the ticket vending machines.

RECEIVE YOUR E-TICKET BY EMAIL
Receive your electronic ticket by email in PDF format. Print a copy of the e-ticket in advance or carry it in your mobile phone.

PICK UP YOUR BOARDING PASS
Scan the QR code included in your electronic ticket at the ticket gates or pick up the physical ticket at the ticket vending machines and cross through the gates using your boarding pass.

BOARD THE TRAIN
Access the platform, locate your car number corresponding to Non-reserved Seat or Reserved Seat and wait for the boarding call to board the train.


 Hokkaido Shinkansen serving Aomori and Hokuto
Hokkaido Shinkansen serving Aomori and Hokuto
 Tohoku Shinkansen serving Tokyo, Fukushima, Sendai, Morioka and Aomori
Tohoku Shinkansen serving Tokyo, Fukushima, Sendai, Morioka and Aomori
 Tokaido Shinkansen serving Tokyo, Yokohama, Nagoya, Kyoto and Osaka
Tokaido Shinkansen serving Tokyo, Yokohama, Nagoya, Kyoto and Osaka
 Thunderbird Limited Express serving Osaka, Kyoto, Tsuruga, Fukui and Kanazawa
Thunderbird Limited Express serving Osaka, Kyoto, Tsuruga, Fukui and Kanazawa
 Hanshin Main Line and Hanshin Namba Line serving Osaka and Kobe
Hanshin Main Line and Hanshin Namba Line serving Osaka and Kobe
 Hankyu Kyoto Main Line and Hankyu Arashiyama Line serving Osaka and Kyoto
Hankyu Kyoto Main Line and Hankyu Arashiyama Line serving Osaka and Kyoto
 Kintetsu Nara Line serving Osaka and Nara
Kintetsu Nara Line serving Osaka and Nara
 Ginza Line
Ginza Line Skyliner Airport Express serving Narita Airport and Tokyo
Skyliner Airport Express serving Narita Airport and Tokyo
 Midosuji Line
Midosuji Line Rapi:t Airport Express serving Kansai Airport and Osaka
Rapi:t Airport Express serving Kansai Airport and Osaka